
The somatomotor fibers of the radial nerve branch from the main radial nerve at the level of the radial groove of the humerus.Ī lateral part of the posterior compartment of the forearm includes the "lateral wad" muscles brachioradialis and extensores radiales. There are in fact 6 separate compartments on the back (dorsum) of the wrist that contain tendons of muscles that extend (as opposed to flex) the wrist and the fingers and thumb. The radial nerve arises from the posterior cord of the plexus, while the median nerve has contributions from both the lateral and medial cords. Wrist tendinopathy usually affects the extensor tendons and the compartments of the wrist that they fit through.
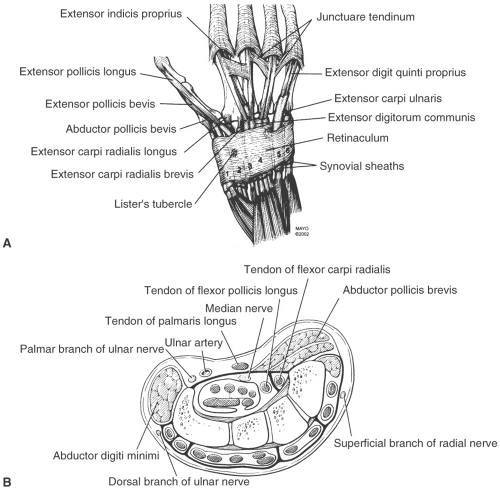
The muscles of the posterior compartment of the forearm are innervated by the radial nerve and median nerve of the brachial plexus. Clinically this study lends insight to the strength of bone-retinaculum-bone autografts and the etiology of extensor carpi ulnaris subluxation.The posterior compartment of the forearm (Extensor compartment of forearm) contains the following muscles: This study offers detailed analysis of the extensor retinaculum compartments and 3-dimensional anatomy of the septal attachments. Compartment 6, which was thought to be the weakest because of clinically observed subluxation of the extensor carpi ulnaris tendon, had stronger failure data than expected. In compartment testing, compartments 1 and 2 had the highest overall resistance to failure and compartment 5 had the lowest.

Septum 1/2 also was found to have the highest failure strength at 51.3 +/- 15.3 N. The fluid distension of extensor tendons sheaths was significantly associated with dorsal radio fractures (p0.008. Septum 1/2 had the largest radial surface area and septum 3/4 had the smallest. The most frequently affected compartments were 2nd and 3rd extensor compartments. Stenosing tendovaginitis of the dorsal and volar compartments of the wrist. The peroneal tendons are located behind the outside portion Small wrist bone (carpal) fractures may result from a fall onto an outstretched (extended) wrist or from a direct blow to the back of the wrist Ligamentous (and Tendon) Injuries of the Hand & Wrist Adam Bakker, M Tendonitis, also known as tendinitis, is the irritation of a tendon. Each tunnel is lined internally by a synovial sheath and separated from one another by fibrous septa. Finally the 6 extensor retinaculum compartments were tested to failure. Compartment 1 contains the abductor pollicis longus (radial / palmar) and extensor pollicis brevis (ulnar / dorsal). All had preoperative tenderness along the extensor carpi ulnaris tendon. The extensor tendon compartments of the wrist are six tunnels which transmit the long extensor tendons from the forearm into the hand They are located on the posterior aspect of the wrist. Next each extensor retinaculum septum was excised as a bone-retinaculum-bone autograft and was tested in tension to failure with a materials testing machine. The musculotendinous junctions of the first extensor compartment tendons (abductor pollicis longus and extensor pollicis brevis tendons) intersect the second. These extensor tendons are held in place inside their compartment by the extensor retinaculum, a strong transverse ligament that the tendons pass under. First, anatomic measurements of the individual extensor retinaculum septums were performed with calipers and a 3-dimensional digitizer. There are in fact 6 separate compartments on the back (dorsum) of the wrist that contain tendons of muscles that extend (as opposed to flex) the wrist and the fingers and thumb. Thirty-four wrists from 24 fresh-frozen and 10 embalmed cadavers were used. This evaluation tool outlines the location of different extensor tendon compartments in the hand and common pathologies seen in each compartment.

It can be difficult to determine the best course of action when evaluating the dorsal wrist tendons. A combination of a wrist orthosis and an oral nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drug was prescribed for 10 days, followed by a personalized rehabilitation. The anatomy of the extensor retinaculum of the wrist has been described previously the purpose of this study was to describe the specific anatomy of the septal attachments on the radius and to investigate the mechanical strength of each septal attachment on the radius and each of the 6 compartments of the extensor retinaculum. Wrist extensor tendinopathies are a less often encountered diagnosis in rehabilitation settings. Extensor compartments were otherwise normal.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
